What Color Is Ribosomes In Animal Cell
Learning Outcomes
- Identify key organelles present only in found cells, including chloroplasts and cardinal vacuoles
- Identify key organelles present simply in animal cells, including centrosomes and lysosomes
At this bespeak, information technology should be articulate that eukaryotic cells have a more complex construction than do prokaryotic cells. Organelles let for various functions to occur in the jail cell at the same fourth dimension. Despite their fundamental similarities, there are some striking differences between animal and constitute cells (see Figure 1).
Brute cells have centrosomes (or a pair of centrioles), and lysosomes, whereas plant cells do not. Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts, plasmodesmata, and plastids used for storage, and a large central vacuole, whereas animal cells do not.
Exercise Question

Figure one. (a) A typical animal cell and (b) a typical plant prison cell.
What structures does a constitute cell have that an animal prison cell does not have? What structures does an animal cell accept that a institute cell does not have?
Show Answer
Plant cells have plasmodesmata, a cell wall, a large cardinal vacuole, chloroplasts, and plastids. Fauna cells have lysosomes and centrosomes.
Plant Cells
The Cell Wall
In Figure 1b, the diagram of a institute jail cell, you come across a structure external to the plasma membrane chosen the cell wall. The cell wall is a rigid roofing that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. Fungal cells and some protist cells also have cell walls.
While the main component of prokaryotic jail cell walls is peptidoglycan, the major organic molecule in the institute jail cell wall is cellulose (Effigy 2), a polysaccharide fabricated upward of long, straight bondage of glucose units. When nutritional information refers to dietary cobweb, it is referring to the cellulose content of food.

Figure 2. Cellulose is a long concatenation of β-glucose molecules continued by a 1–four linkage. The dashed lines at each end of the effigy indicate a series of many more glucose units. The size of the page makes information technology incommunicable to portray an entire cellulose molecule.
Chloroplasts

Figure 3. This simplified diagram of a chloroplast shows the outer membrane, inner membrane, thylakoids, grana, and stroma.
Like mitochondria, chloroplasts also take their ain Dna and ribosomes. Chloroplasts function in photosynthesis and can be plant in photoautotrophic eukaryotic cells such as plants and algae. In photosynthesis, carbon dioxide, h2o, and light free energy are used to brand glucose and oxygen. This is the major difference betwixt plants and animals: Plants (autotrophs) are able to make their own food, like glucose, whereas animals (heterotrophs) must rely on other organisms for their organic compounds or food source.
Similar mitochondria, chloroplasts have outer and inner membranes, but within the space enclosed by a chloroplast'southward inner membrane is a set of interconnected and stacked, fluid-filled membrane sacs called thylakoids (Effigy 3). Each stack of thylakoids is called a granum (plural = grana). The fluid enclosed by the inner membrane and surrounding the grana is called the stroma.
The chloroplasts contain a green paint called chlorophyll, which captures the energy of sunlight for photosynthesis. Like plant cells, photosynthetic protists also have chloroplasts. Some leaner also perform photosynthesis, but they exercise not have chloroplasts. Their photosynthetic pigments are located in the thylakoid membrane within the cell itself.
Endosymbiosis
We have mentioned that both mitochondria and chloroplasts contain Deoxyribonucleic acid and ribosomes. Have you lot wondered why? Strong evidence points to endosymbiosis every bit the explanation.
Symbiosis is a relationship in which organisms from ii dissever species live in close association and typically exhibit specific adaptations to each other. Endosymbiosis (endo-= inside) is a human relationship in which one organism lives inside the other. Endosymbiotic relationships abound in nature. Microbes that produce vitamin K live inside the human being gut. This relationship is benign for the states considering we are unable to synthesize vitamin One thousand. Information technology is also benign for the microbes because they are protected from other organisms and are provided a stable habitat and abundant food by living within the large intestine.
Scientists have long noticed that bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts are similar in size. We likewise know that mitochondria and chloroplasts have Dna and ribosomes, simply as bacteria exercise. Scientists believe that host cells and leaner formed a mutually benign endosymbiotic relationship when the host cells ingested aerobic bacteria and cyanobacteria but did not destroy them. Through development, these ingested leaner became more specialized in their functions, with the aerobic bacteria becoming mitochondria and the photosynthetic bacteria becoming chloroplasts.
Try It
The Central Vacuole
Previously, nosotros mentioned vacuoles every bit essential components of plant cells. If you lot look at Figure 1b, you will see that constitute cells each have a big, fundamental vacuole that occupies most of the cell. The central vacuole plays a key office in regulating the cell'southward concentration of water in changing ecology weather. In found cells, the liquid inside the central vacuole provides turgor pressure, which is the outward pressure caused past the fluid within the cell. Accept you ever noticed that if you forget to water a plant for a few days, information technology wilts? That is because as the water concentration in the soil becomes lower than the water concentration in the plant, water moves out of the central vacuoles and cytoplasm and into the soil. As the central vacuole shrinks, it leaves the prison cell wall unsupported. This loss of back up to the prison cell walls of a found results in the wilted advent. When the central vacuole is filled with water, it provides a depression energy ways for the plant cell to expand (as opposed to expending energy to actually increase in size). Additionally, this fluid tin deter herbivory since the bitter taste of the wastes information technology contains discourages consumption by insects and animals. The central vacuole besides functions to store proteins in developing seed cells.
Animal Cells
Lysosomes

Figure four. A macrophage has phagocytized a potentially pathogenic bacterium into a vesicle, which then fuses with a lysosome within the prison cell so that the pathogen can be destroyed. Other organelles are present in the cell, but for simplicity, are not shown.
In animal cells, the lysosomes are the cell'south "garbage disposal." Digestive enzymes within the lysosomes aid the breakdown of proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids, and even worn-out organelles. In unmarried-celled eukaryotes, lysosomes are of import for digestion of the food they ingest and the recycling of organelles. These enzymes are active at a much lower pH (more acidic) than those located in the cytoplasm. Many reactions that take place in the cytoplasm could not occur at a depression pH, thus the advantage of compartmentalizing the eukaryotic prison cell into organelles is apparent.
Lysosomes also utilise their hydrolytic enzymes to destroy disease-causing organisms that might enter the jail cell. A good example of this occurs in a group of white claret cells chosen macrophages, which are role of your trunk's immune system. In a procedure known as phagocytosis, a section of the plasma membrane of the macrophage invaginates (folds in) and engulfs a pathogen. The invaginated section, with the pathogen inside, and so pinches itself off from the plasma membrane and becomes a vesicle. The vesicle fuses with a lysosome. The lysosome's hydrolytic enzymes then destroy the pathogen (Figure 4).
Extracellular Matrix of Animal Cells

Figure 5. The extracellular matrix consists of a network of substances secreted by cells.
Near animal cells release materials into the extracellular infinite. The main components of these materials are glycoproteins and the protein collagen. Collectively, these materials are called the extracellular matrix (Figure 5). Non simply does the extracellular matrix hold the cells together to form a tissue, simply information technology too allows the cells within the tissue to communicate with each other.
Blood clotting provides an instance of the part of the extracellular matrix in cell communication. When the cells lining a blood vessel are damaged, they display a protein receptor called tissue factor. When tissue factor binds with another factor in the extracellular matrix, information technology causes platelets to attach to the wall of the damaged blood vessel, stimulates adjacent smoothen muscle cells in the claret vessel to contract (thus constricting the blood vessel), and initiates a serial of steps that stimulate the platelets to produce clotting factors.
Intercellular Junctions
Cells tin can also communicate with each other past directly contact, referred to as intercellular junctions. In that location are some differences in the ways that plant and animal cells practise this. Plasmodesmata (singular = plasmodesma) are junctions betwixt plant cells, whereas animate being prison cell contacts include tight and gap junctions, and desmosomes.
In general, long stretches of the plasma membranes of neighboring constitute cells cannot bear upon ane another because they are separated by the cell walls surrounding each cell. Plasmodesmata are numerous channels that pass between the jail cell walls of next constitute cells, connecting their cytoplasm and enabling betoken molecules and nutrients to exist transported from cell to prison cell (Figure 6a).
A tight junction is a watertight seal between two adjacent animal cells (Effigy 6b). Proteins hold the cells tightly against each other. This tight adhesion prevents materials from leaking between the cells. Tight junctions are typically found in the epithelial tissue that lines internal organs and cavities, and composes most of the pare. For instance, the tight junctions of the epithelial cells lining the urinary float preclude urine from leaking into the extracellular space.
Also found only in animal cells are desmosomes, which act like spot welds between adjacent epithelial cells (Figure 6c). They keep cells together in a canvas-like formation in organs and tissues that stretch, similar the peel, heart, and muscles.
Gap junctions in animal cells are like plasmodesmata in found cells in that they are channels between next cells that permit for the send of ions, nutrients, and other substances that enable cells to communicate (Figure 6d). Structurally, however, gap junctions and plasmodesmata differ.
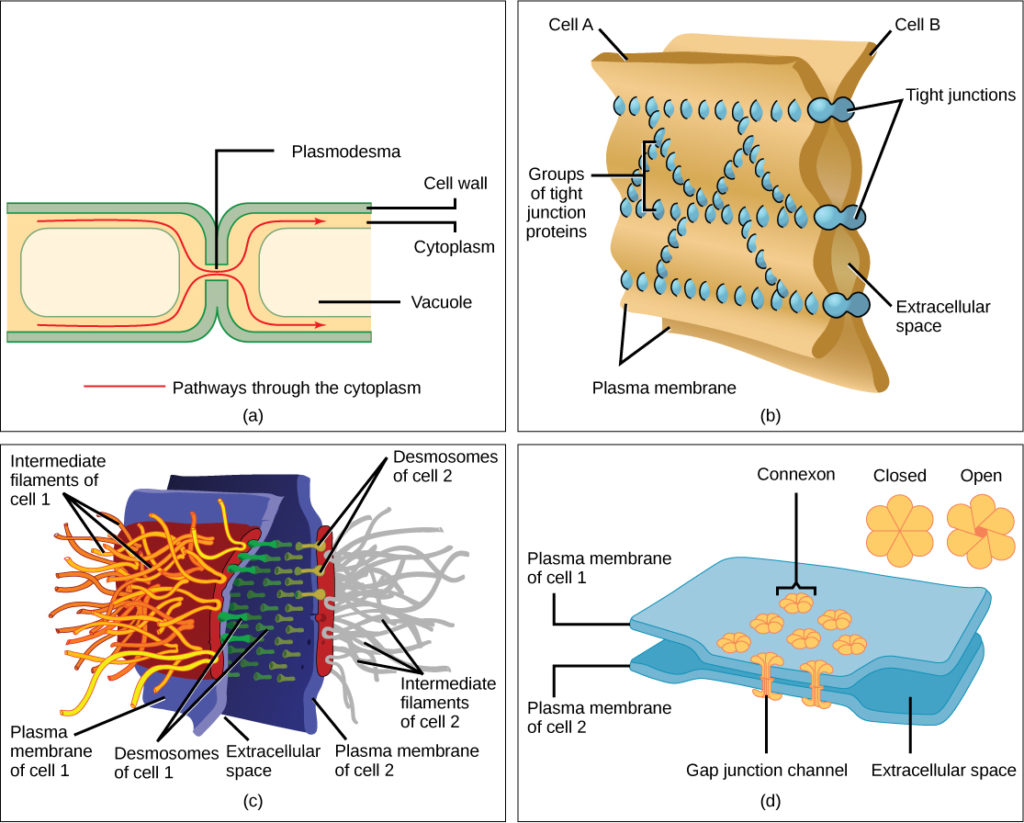
Effigy 6. There are iv kinds of connections between cells. (a) A plasmodesma is a channel between the prison cell walls of two adjacent plant cells. (b) Tight junctions bring together side by side animal cells. (c) Desmosomes join two fauna cells together. (d) Gap junctions deed as channels between brute cells. (credit b, c, d: modification of work by Mariana Ruiz Villareal)
Contribute!
Did y'all accept an idea for improving this content? We'd love your input.
Meliorate this pageLearn More
Source: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wm-nmbiology1/chapter/animal-cells-versus-plant-cells/
Posted by: ornelasproffecanded.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Color Is Ribosomes In Animal Cell"
Post a Comment